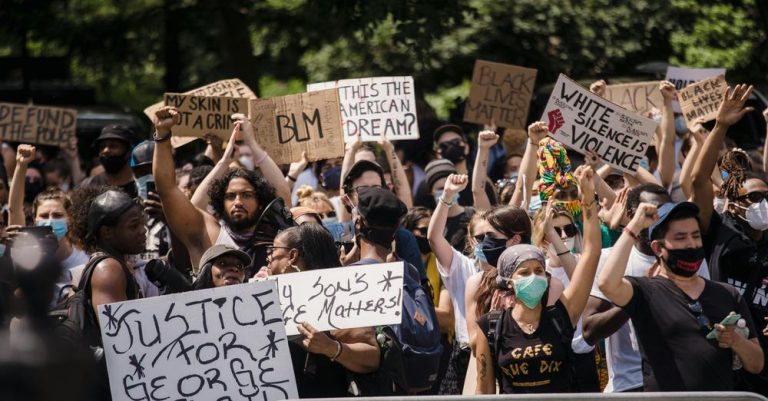Public protests and social movements are powerful catalysts for change, influencing everything from local policies to global human rights standards. Understanding these phenomena requires a look at their historical context, key elements, and the impact they have on society. In this article, we’ll explore the evolution of public protests, the dynamics of social movements, and their profound effects on both policy and culture.
The Evolution of Public Protests
Early Forms of Protest
Protests have been a part of human history for centuries. Ancient societies, from the Roman Empire to medieval kingdoms, saw various forms of public dissent. These early protests often revolved around grievances related to governance, economic hardships, or social injustices.
The Role of Technology in Modern Protests
In recent decades, technology has transformed the nature of protests. The rise of the internet, social media, and mobile communication has enabled activists to organize more effectively, reach a global audience, and amplify their voices. Platforms like Twitter and Facebook have become crucial tools for mobilizing support and documenting events in real-time.
Key Elements of Social Movements
Leadership and Organization
Successful social movements often have strong leadership and a clear organizational structure. Leaders provide direction, inspire participants, and negotiate with authorities. Organizations, ranging from grassroots groups to large NGOs, coordinate activities and manage resources.
Goals and Objectives
Every social movement has specific goals. These might include policy changes, social justice, or raising awareness about a particular issue. The clarity of these objectives helps in rallying support and measuring the movement’s success.
Case Studies of Major Social Movements
The Civil Rights Movement
One of the most significant social movements in history, the Civil Rights Movement in the United States, fought against racial segregation and discrimination. Leaders like Martin Luther King Jr. and organizations such as the NAACP played crucial roles in advocating for equality and justice.
The Women’s Rights Movement
The Women’s Rights Movement has been instrumental in advocating for gender equality. From the suffrage movement of the early 20th century to the contemporary push for equal pay and reproductive rights, this movement has achieved significant milestones in advancing women’s rights.
The Environmental Movement
The Environmental Movement, highlighted by events like Earth Day and organizations such as Greenpeace, focuses on environmental conservation and combating climate change. This movement has led to substantial policy changes and increased global awareness about environmental issues.
Recent Protests: The Arab Spring and Beyond
The Arab Spring was a series of anti-government protests that spread across the Arab world in the early 2010s. It demonstrated the power of social media in facilitating large-scale uprisings and has inspired subsequent movements in various regions.
Impact of Social Movements
Legislative Changes
Social movements often lead to significant legislative changes. For instance, the LGBTQ+ rights movement has resulted in the legalization of same-sex marriage in many countries. Similarly, environmental movements have prompted stricter environmental regulations and sustainability initiatives.
Social and Cultural Impact
Beyond legislation, social movements shape societal norms and cultural attitudes. They challenge established paradigms, promote inclusivity, and influence public discourse on various issues.
Challenges Faced by Social Movements
Government Repression
Many social movements face repression from governments. Authorities may use force, censorship, or legal measures to undermine protests and suppress dissent. Such actions can hinder progress and lead to further conflict.
Internal Conflicts
Movements may also struggle with internal conflicts, such as disagreements among leaders or factions within the group. These conflicts can affect the movement’s coherence and effectiveness.
The Role of Media in Public Protests
Traditional Media
Traditional media, including newspapers, television, and radio, play a role in shaping public perception of protests. They provide coverage and analysis, which can either support or criticize the movement’s objectives.
Social Media and Its Influence
Social media has revolutionized how protests are covered and perceived. Platforms like Twitter and Instagram allow for real-time updates, viral content, and broader engagement. However, they also pose challenges, such as the spread of misinformation and echo chambers.
Public Perception and Support
Factors Influencing Public Opinion
Public support for protests can be influenced by various factors, including media portrayal, the movement’s perceived legitimacy, and the socioeconomic context. Effective communication and transparent goals help in garnering broader support.
The Role of Grassroots Organizations
Grassroots organizations are vital in mobilizing local communities and providing support for larger movements. Their on-the-ground efforts help in building momentum and sustaining the movement over time.
Globalization and Social Movements
The Spread of Ideas Across Borders
Globalization has facilitated the spread of social movement ideas across borders. Activists can draw inspiration from movements in other countries and build international solidarity to address global issues.
International Solidarity
International solidarity plays a crucial role in amplifying the impact of social movements. Global support can put pressure on governments and institutions, leading to more significant changes.
Future Trends in Social Movements
Emerging Issues and Movements
As society evolves, new issues and movements will emerge. Topics such as digital rights, artificial intelligence, and global health may become central to future social movements.
The Role of Technology in Future Protests
Technology will continue to shape the nature of protests. Innovations in communication, data analysis, and virtual reality could transform how movements organize, advocate, and engage with supporters.